Unlocking New Horizons in Embedded Technology with M.2
In contemporary embedded system design, various miniaturized interfaces are observed, such as mSATA, miniPCIe, and the more modern M.2 interface. These interfaces are closely related to I/O and data transfer technologies within computer hardware architectures and reflect the trend of technological evolution. Driven by demands for faster data processing, the evolution of miniaturized interfaces has transitioned from mSATA and miniPCIe to the M.2 interface. This shift underscores the need for stronger, more compact computer interfaces and highlights the importance of understanding the evolution of each interface and their respective advantages.
Revisiting the Role of miniPCIe in Modern Embedded Systems
Although the M.2 interface represents the future of compact and robust technologies, miniPCIe (Mini PCI Express) continues to play a critical role in many embedded systems due to its versatility and established position in the industry. MiniPCIe is a miniaturized version of the PCI Express interface, widely used to expand the capabilities of compact systems. Unlike mSATA, miniPCIe can transmit data via PCI Express lanes and supports USB 2.0 signals, making it suitable not only for storage expansion but also for integrating other peripherals such as WiFi, Bluetooth, and mobile network cards..png)
The Rise and Evolution of M.2
As demands for higher performance and greater miniaturization continue to grow, the M.2 interface has gradually replaced mSATA and miniPCIe to become the preferred interface for many new products. M.2 utilizes up to four PCIe 3.0 lanes, NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express), the SATA protocol, and USB 3.0 signals, providing faster data transfer speeds than ever before. This high-speed capability makes M.2 especially suitable for high-end technology applications such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) or real-time processing, which require low latency and reliable solutions to ensure smooth operation of mission-critical applications.
The M.2 Interface: Advancing Expansion Slots
The M.2 slot, a specification for internal expansion cards on motherboards, was first unveiled by Intel in 2012 under the designation "Next Generation Form Factor" (NGFF). This interface has transformed the landscape of internal computer expansions, supporting a wide array from simple wireless network cards to sophisticated AI accelerators. Its superior speed is attributed to the capability to fully utilize PCI Express lanes, significantly outpacing its predecessor, mSATA. On modern motherboards, M.2 slots can leverage two to four PCIe lanes, with each lane on PCIe 4.0 capable of achieving a staggering 16Gb/s, rendering M.2 devices exponentially faster than mSATA equivalents.
Enhanced Flexibility and Efficiency of M.2
The M.2 interface surpasses mSATA in terms of flexibility, accommodating a range of bus interfaces including PCIe, SATA, and USB. This versatility extends to its logical interface as well, which supports both NVMe and SATA protocols, ensuring compatibility with both cutting-edge and legacy technologies. The practical applications of M.2 are diverse, enabling the deployment of solid-state drives (SSDs), wireless connectivity cards, various I/O expansion cards, and high-performance accelerator cards tailored for demanding computational workloads.
Advantages of M.2 Technology
M.2 stands out due to its compact size—the smallest M.2 modules are 18% smaller than the most compact miniPCIe devices. The design of M.2 slots also allows for flexibility in card lengths, accommodating multiple sizes to fit different system requirements. Energy efficiency is another key benefit, with power consumption capped at 7 watts, making M.2 an environmentally friendly choice for system builders. In terms of performance, M.2 devices deliver speeds from 50% to 650% faster than traditional SATA devices, courtesy of the NVMe protocol and the bandwidth available through PCIe 4.0’s up to four lanes.
This redefined M.2 interface showcases its pivotal role in pushing forward the performance boundaries of modern computing systems, ensuring they meet the rigorous demands of advanced applications while maintaining efficiency and compactness.
M.2 Expansion Slots: Different Key Types
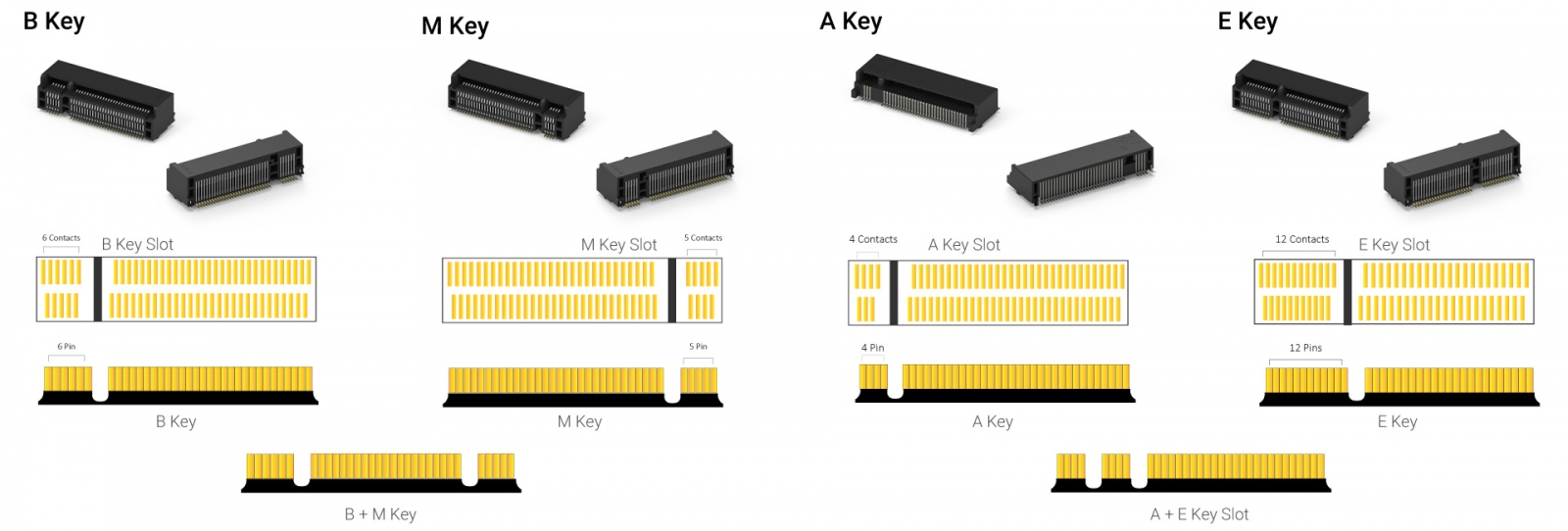
| Key Type | Pin Gap Location | Common Usage | Interface Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| A Key | 4 pins at left | WiFi, Bluetooth, Cellular modules | 2x PCIe x1, USB 2.0, I2C, Display Port (DP) x4 |
| E Key | 12 pins at left | WiFi, Bluetooth, Cellular modules | 2x PCIe x1, USB 2.0, I2C, SDIO, UAT, PCM, CNVi |
| A+E Key | 4 pins and 12 pins at left | Compatible with both A and E key slots | Combines A and E Key features, supporting both sets of interfaces |
| B Key | 6 pins at left | SATA, PCIe x2, SSD | PCIe x2, SATA, USB 2.0/3.0, UIM, HSIC, SSIC, I2C, SMBus |
| M Key | 5 pins at right | PCIex4, NVMe SSD | PCIe x4, SATA, SMBus |
| B+M Key | 6 pins at left and 5 pins at right | Compatible with both B and M key slots | Combines B and M Key features, allowing compatibility with a wider range of M.2 slots on motherboards |
M.2 Form Factors
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Initial Commercial Width | 22 mm |
| Initial Commercial Lengths (mm) | 30, 42, 60, 80, 110 |
| Standard Widths (mm) | 12, 16, 22, 30 |
| Standard Lengths (mm) | 16, 26, 30, 38, 42, 60, 80, 110 |
Expansion Capabilities of miniPCIe and M.2
MiniPCIe and M.2 interfaces offer unique solutions for expanding the functionalities of embedded systems. MiniPCIe, with its compact size and versatility, is suitable for portable and industrial devices needing network and storage enhancements. In contrast, M.2 excels in applications requiring extensive data processing and high-speed computation, such as advanced SSD storage and high-performance computing platforms.
The integration and advancements of these technologies underscore the need for reliable connectors. ATTEND Technology’s high-quality M.2 and miniPCIe connectors ensure that systems can fully utilize these advanced technologies, enhancing the adaptability and performance of embedded computing applications. By understanding the specific roles and advantages of M.2 and miniPCIe, stakeholders can make informed decisions to select the technology that best meets their needs.
The integration and advancements of these technologies underscore the need for reliable connectors. ATTEND Technology’s high-quality M.2 and miniPCIe connectors ensure that systems can fully utilize these advanced technologies, enhancing the adaptability and performance of embedded computing applications. By understanding the specific roles and advantages of M.2 and miniPCIe, stakeholders can make informed decisions to select the technology that best meets their needs.
The Role of M.2 and miniPCIe in Embedded Systems
M.2 and miniPCIe provide functionalities that extend beyond traditional storage solutions. Both technologies support a wide range of applications from basic wireless network cards to complex AI accelerators, making them indispensable parts of modern embedded technologies.
High Flexibility of the M.2 Interface
The M.2 interface supports PCI Express lanes, SATA, and USB, making it highly flexible for various applications. For instance, M.2 can use both NVMe and SATA storage protocols to support modern and legacy technologies, offering seamless compatibility. The physical form factor of M.2 also supports a variety of expansion card sizes, including different length options, making it suitable for devices ranging from personal computers to industrial applications.
Wide Applications of miniPCIe
Meanwhile, miniPCIe, with its miniature design, remains highly useful in applications where space is limited. It not only supports high-speed data transmission via PCIe lanes but also integrates USB 2.0 signals, enabling support for various functions including wireless networks, Bluetooth, and other I/O expansions. This versatility makes miniPCIe an ideal choice for many portable and industrial devices, particularly where cost and space efficiency are crucial.
Comparison of mini PCIe and M.2 Card Applications
To better understand the specific roles of mini PCIe and M.2 expansion cards and how ATTEND's connectors support these roles, here is a detailed comparison:
| Feature | mini PCIe Card Solutions | M.2 Card Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi/ Networking | Enhances wireless connectivity, suitable for general applications | Provides superior high-speed wireless capabilities, ideal for intensive data communication |
| Storage | Offers additional storage options, generally slower speeds | Supports high-speed storage solutions like NVMe, essential for high-performance applications |
| I/O Ports | Adds necessary ports for various peripherals, ideal for expanding connectivity in compact systems | Delivers faster and more versatile port expansions, catering to modern, high-speed interfaces |
| Graphics/Video | Suitable for basic display expansions | Supports advanced graphics and video processing, necessary for high-definition content |
Integrating ATTEND Technology’s Connectors
To maximize the potential of M.2 and miniPCIe, ATTEND Technology provides connectors that ensure these expansion cards operate stably and effectively in various embedded systems. These connectors are rigorously designed to meet the demands of high-speed data transmission and multifunctional integration, ensuring connection reliability and durability.Features and Advantages of M.2 and miniPCIe Connectors:
.png)
M.2 Connectors:
- Compatibility: Meets PCI-SIG PCIe M.2 specs, supporting PCI Express 3.0, SATA 3.0, and USB 3.0.
- Multiple Keying Options: Supports various M.2 card types with A, B, E, and M keys for diverse applications.
- One-action Latch: Allows quick and economical installation.
- High-Speed Transmission: Uses up to four PCIe lanes for top data transfer rates, perfect for high-performance needs.
.png)
miniPCIe Connectors:
- Voltage: 1.5 V or 3.3 V
- Pin Count: 52 pins
- Speed: Compatible with PCI Express 1.0 x1 (250 MB/s) and PCI Express 2.0 x1 (500 MB/s)
- Mounting Options: Features single or dual latches and screws for secure installation.
- Versatility: Facilitates high-speed PCIe and USB 2.0 transmissions for various I/O expansions.
Conclusion
M.2 and miniPCIe each play an indispensable role in embedded systems, and ATTEND Technology’s connectors provide a solid foundation for the implementation of these technologies. Using high-quality connectors ensures that expansion cards not only provide the necessary functionalities but also maintain the overall stability and reliability of the systems. As technology progresses, ATTEND Technology continues to develop connectivity solutions that support the latest standards in embedded technologies, pushing embedded systems towards a future of higher efficiency and more compact designs.By thoroughly understanding and appropriately utilizing these technologies, it is possible to develop more advanced, powerful embedded solutions that drive innovation and progress across various industries. Looking forward, as the demand for faster data processing, lower latencies, and more compact designs grows, M.2 and miniPCIe are expected to continue playing a pivotal role in embedded systems.
We'd love to hear your thoughts on this post and any topics you'd like us to explore in the future.
Send your suggestions to marketing@attend.com.tw
|

.png)